Share this
What is a Gerotor Pump? A Comprehensive Overview
by Glenn Mann on Aug 4, 2023 8:35:46 AM
When it comes to the field of engineering, the concept of a gerotor is widely used in the production of various machines and devices, but what exactly is a gerotor pump and how does it work?
In this blog, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of the gerotor pump, including its design, functionality, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
What is a Gerotor Pump?
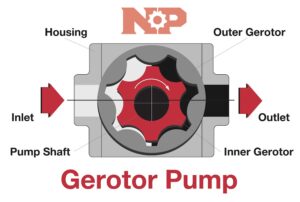
A gerotor pump is a type of positive displacement pump consisting of an outer gerotor, an inner gerotor, and a housing.
As you can see in the illustration below, the outer gerotor has one tooth more than the inner gerotor and has a convex cycloidal profile on its external surface. The inner gerotor has a concave cycloidal profile on its internal surface and is mounted off-center within the outer gerotor.
The two gerotors are positioned such that the convex and concave surfaces are in contact with each other.
The housing, which is typically made of cast iron or aluminum, contains the rotors and provides the necessary support.
How Does a Gerotor Pump Work?
A gerotor pump operates by trapping fluid between the rotor teeth and the housing, creating a seal. As the rotors rotate, the fluid is carried around the outer rotor and into the inner rotor, where it is then discharged. The amount of fluid pumped per revolution is dependent on the size and shape of the rotors and the housing, as well as the speed of rotation.
Gerotor Pump Advantages & Disadvantages
In this section, we explore the advantages and disadvantages of gerotor pumps to help you determine whether a gerotor pump is the best choice for your specific pumping needs.
Advantages of Gerotor Pumps
Gerotor pumps offer several advantages over other types of pumps, including:
- High Efficiency: Gerotor pumps offer high volumetric efficiency, meaning they can move a high volume of fluid per revolution. They have volumetric efficiencies of up to 98%, making them one of the most efficient types of displacement pumps.
- Low Noise & Vibration: Gerotor pumps operate with low noise and vibration levels, making them ideal for applications that require quiet operation. They generate less noise and vibration than other types of pumps, such as gear or vane pumps.
- Compact Size: Gerotor pumps are relatively compact and lightweight compared to other types of positive displacement pumps. They take up less space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- High-Pressure Capabilities: Gerotor pumps can operate at high pressures, with maximum pressure ratings of up to 10,000 PSI.
- Self-Priming: Gerotor pumps are self-priming, meaning they can operate without the need for external priming. This makes them ideal for applications where the fluid being pumped may contain air or gas.
Disadvantages of Gerotor Pumps
As with any type of pump, there are disadvantages. The main disadvantages of gerotor pumps include:
- Limited Viscosity Range: Gerotor pumps have a limited range of viscosity that they can pump effectively. They’re best suited for pumping low to medium-viscosity fluids, such as oil, fuel, or water. They’re not well-suited for pumping high-viscosity fluids, such as molasses or honey.
- Limited Suction Capability: Gerotor pumps have a limited suction capability, which means they can’t draw fluid from a deep source or a high elevation. They require a positive head of fluid to operate efficiently.
- Wear & Tear: Gerotor pumps can experience wear and tear over time due to the close tolerances between the rotors and the housing. This can lead to decreased efficiency and increased maintenance costs.
Gerotor Pump Applications
Gerotors are used in a variety of industrial and automotive applications, particularly in hydraulic systems where precise and efficient fluid flow is required. They can also be useful in other non-industrial applications, such as power steering systems for vehicles, due to their low sound levels compared to rotary pumps operating at higher speeds (noise can be an issue when running machines close to people).
Other common applications of gerotors include:
- Engine oil pumps and fuel pumps in automobiles and other internal combustion engines
- Lubrication systems in compressors, gearboxes, and other industrial machinery
- Hydraulic elevators and lifts in industrial and commercial buildings
- High-pressure hydraulic systems in aerospace and defense applications
- Vacuum pumps and blowers in a wide range of industries
- Positive displacement compressors for gasses and other compressible fluids
- Hydraulic motors for driving conveyor belts, mixers, and other industrial machinery
- Coolant pumps for engines and other heat-generating equipment
- Braking systems in off-road vehicles and heavy equipment
These are just a few of the many applications for gerotors, which are valued for their efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle a wide range of fluid viscosities.
Gerotor Pumps: Efficient & Versatile Pumping Systems
Overall, gerotor pumps offer a reliable, quiet, and efficient pumping solution for a wide range of applications.
When selecting a pump for your application, it’s important to consider your specific pumping needs, along with the advantages and disadvantages of the pump types you’re considering to determine the best fit.
Ready to learn more? Check out our other resources!


Comments (4)